前言
这一节就简单讲一讲FastThreadLocal的使用,以及为什么FastThreadLocal比jdk原生的ThreadLocal快。
如果你有ThreadLocal的使用经验,那么相信FastThreadLocal根本不需要教了,核心api基本一样。
关于ThreadLocal和FastThreadLocal都是线程独享变量这种基础理论我就不讲了,建议阅读者有一定的ThreadLocal理论知识。
Netty Version:4.1.6
实验代码
这里我就自定义实验代码,你如果想有比较完整的体验,也可以用Netty提供的单元测试代码:
FastThreadLocalTest.java
import io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocal;
import io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocalThread;
public class FastThreadLocalTest {
private static FastThreadLocal<Object> threadLocal0 = new FastThreadLocal<Object>() {
@Override
protected Object initialValue() {
return new Object();
}
@Override
protected void onRemoval(Object value) throws Exception {
System.out.println("onRemoval");
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
new FastThreadLocalThread(() -> {
Object object = threadLocal0.get();
// .... do with object
System.out.println(object);
threadLocal0.set(new Object());
while (true) {
threadLocal0.set(new Object());
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
new FastThreadLocalThread(() -> {
Object object = threadLocal0.get();
// ... do with object
System.out.println(object);
while (true) {
System.out.println(threadLocal0.get() == object);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
输出结果:
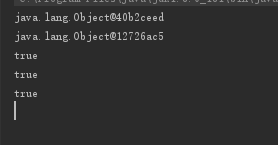
- 两个线程的值不互相干扰,说明变量是线程独享的。
跟进源码
FastThreadLocalThread简介
为啥要先看看FastThreadLocalThread?因为实际上只有FastThreadLocalThread类型的线程才能使用FastThreadLocal,如果是普通线程,就算调用FastThreadLocal的get、set方法,最终用的还是jdk原生的ThreadLocal。
先来看看它的继承关系:
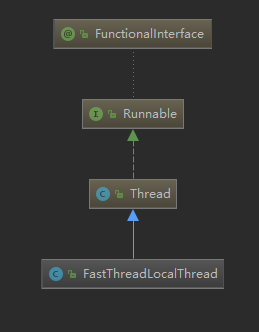
- 继承了Thread,说明是一种线程。
再来看看它的属性,只有一个:
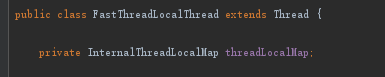
- 每个FastThreadLocalThread都维护了一个InternalThreadLocalMap。
其中,FastLocalThread比ThreadLocal快的原因就在于属性的数据结构、查找算法。下面就来看看FastLocalThread的InternalThreadLocalMap。
InternalThreadLocalMap简介
看看它的继承关系和属性:
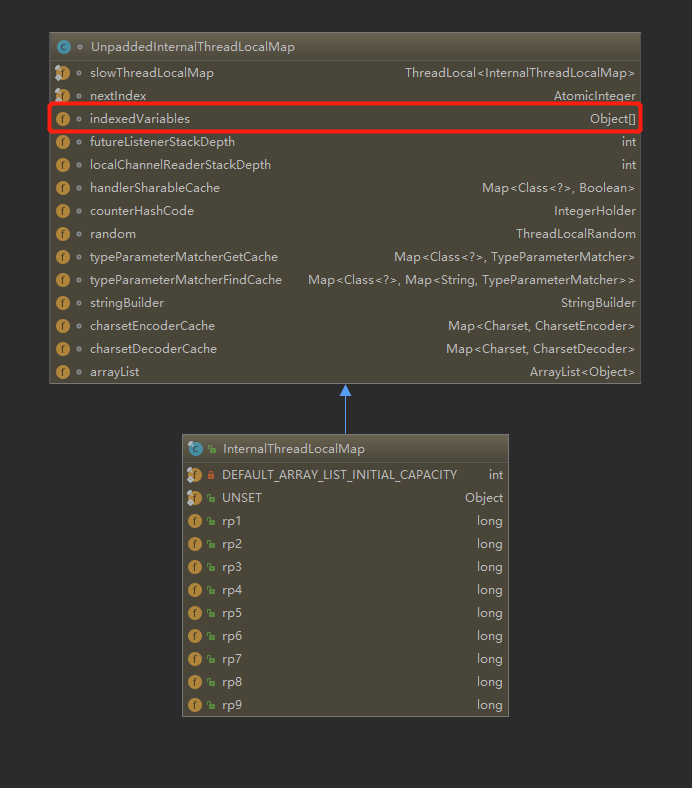
暂时先无视其它属性,indexedVariables就是最终存储线程私有变量的地方。它是个Object数组,这使得根据index获取Object等情况时时,复杂度都为O(1),比ThreadLocal的hash算法要快。
其余方法、属性等遇到自然就懂了,这里先不赘述。
把map、set等结构转成数组这种优化方法在Netty中也不是第一次见了,在创建NioEventLoop的时候也遇到过一次,忘记的可以回去看看。
顺便看看它的构造方法,后面会遇到就不再重复跟进了:
io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap#newIndexedVariableTable
private InternalThreadLocalMap() {
super(newIndexedVariableTable());
}
private static Object[] newIndexedVariableTable() {
Object[] array = new Object[32];
Arrays.fill(array, UNSET);
return array;
}
- 初始大小是32,不够的时候会扩容。
上面这些到下面FastThreadLocal都会用到,建议不熟悉的自行多补充。
FastThreadLocal的创建
看看FastThreadLocal的构造方法:
io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocal#FastThreadLocal
public FastThreadLocal() {
// 从InternalThreadLocalMap中
index = InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex();
}
- 如果建了多个FastThreadLocal就相当于线程的有多个私有变量,这个index就是标识每一个唯一的私有变量,后面获取该变量时,就是根据线程引用+index来获取的。
跟进InternalThreadLocalMap.nextVariableIndex方法看看:
io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap#nextVariableIndex
public static int nextVariableIndex() {
int index = nextIndex.getAndIncrement();
if (index < 0) {
nextIndex.decrementAndGet();
throw new IllegalStateException("too many thread-local indexed variables");
}
return index;
}
- 就是自增id。
FastThreadLocal的构造就是这么简单,但这个index仍然非常关键,大部分方法都是围绕着这个index转的,下面就逐渐见识到这一点了。
FastThreadLocal的get方法
跟进FastThread的get方法,此处【坐标1】:
io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocal#get()
public final V get() {
return get(InternalThreadLocalMap.get());
}
先跟进InternalThreadLocalMap.get():
io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap#get
public static InternalThreadLocalMap get() {
// 取到当前线程
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
if (thread instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) {
// FastThreadLocalThread专属
return fastGet((FastThreadLocalThread) thread);
} else {
// 从jdk的ThreadLocal的map中获取,写博客的时候再跟
return slowGet();
}
}
- 这段代码就体现了FastThreadLocal是FastThreadLocalThread专属的。
这里继续跟进fastGet方法:
io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap#fastGet
// FastThreadLocalThread
private static InternalThreadLocalMap fastGet(FastThreadLocalThread thread) {
// 获取每个线程独立维护的InternalThreadLocalMap对象
InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap = thread.threadLocalMap();
// 一开始threadLocalMap可能为null
if (threadLocalMap == null) {
// 这里的new InternalThreadLocalMap上面讲过了
// 默认就是Object[32]
thread.setThreadLocalMap(threadLocalMap = new InternalThreadLocalMap());
}
return threadLocalMap;
}
- 最终返回一个变量集合。
拿到变量集合,即InternalThreadLocalMap对象后,视角重新转回到【坐标1】的代码,跟外层的get方法:
io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocal#get(io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap)
public final V get(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
// 根据index返回对象
Object v = threadLocalMap.indexedVariable(index);
if (v != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
// 不为空则返回
return (V) v;
}
// 如果是第一次,则为UNSET,这时候就先初始化(不是创建)InternalThreadLocalMap+对象并返回
return initialize(threadLocalMap);
}
跟进indexedVariable看看是不是之前说的那么回事:
io.netty.util.internal.UnpaddedInternalThreadLocalMap#indexedVariables
public Object indexedVariable(int index) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
return index < lookup.length? lookup[index] : UNSET;
}
- 就是根据index获取到对象。
返回到上上面的get方法,跟进initialize方法,看看如果取到的值为UNSET时会做什么:
io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocal#initialize
private V initialize(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap) {
V v = null;
try {
// 调用我们覆写的initialValue构建对象
v = initialValue();
} catch (Exception e) {
PlatformDependent.throwException(e);
}
// 设置index和值的对应关系,若数组大小不够,则扩容
threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, v);
// 添加到删除集合中,比如你想清空该线程的所有变量就会用到
addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
return v;
}
- 注意initialValue方法就是调用实验代码覆写的方法构造对象。
继续跟进setIndexedVariable方法:
io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap#setIndexedVariable
public boolean setIndexedVariable(int index, Object value) {
Object[] lookup = indexedVariables;
// 设置index和value的对应关系
if (index < lookup.length) {
Object oldValue = lookup[index];
lookup[index] = value;
return oldValue == UNSET;
} else {
// 扩容(2的幂次方)
expandIndexedVariableTableAndSet(index, value);
return true;
}
}
- 就是根据数组下标获取到元素然后返回。
好了,现在我们已经了解到FastThreadLocal的get方法流程了,接下来就是要看看它的set方法了。
FastThreadLocal的set方法
跟进FastThreadLocal的set方法:
public final void set(V value) {
if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
// 设置index+value数组关系
set(InternalThreadLocalMap.get(), value);
} else {
// 删除当前index的对象
remove();
}
}
- InternalThreadLocalMap.get()上面讲过了,这里不再赘述。
- 其中remove()在删除元素后,还会回调实验代码的onRemoval方法,有兴趣的就自己跟进一下。
继续跟进set方法:
io.netty.util.concurrent.FastThreadLocal#set(io.netty.util.internal.InternalThreadLocalMap, V)
public final void set(InternalThreadLocalMap threadLocalMap, V value) {
// 判断对象是否是UNSET对象(实际上还是Object,但是引用地址不同)
if (value != InternalThreadLocalMap.UNSET) {
// 保存index和元素的对应关系,上面也讲过了
if (threadLocalMap.setIndexedVariable(index, value)) {
// 上面的initialize也遇到这个方法了,可见每次设置之后都要执行,主要是便于removeall方法一次性清空
addToVariablesToRemove(threadLocalMap, this);
}
} else {
// 删除当前index的对象
remove(threadLocalMap);
}
}
setIndexedVariable执行返回true,就表示成功设置线程的私有变量了。
小结
- FastThreadLocal的使用方法其实跟Thread基本一致,但是使用FastThreadLocal的重要前提是线程必须是FastThreadLocalThread,否则依然是用jdk原生的ThreadLocal。
- FastThreadLocal之所以比ThreadLocal快,主要是因为前者数据结构是数组,后者数据结构为哈希,对于根据index获取值、设置值这种简单操作,使用数组的复杂度更低。
- 这是第二次遇到通过更改jdk原生数据结构来达到优化目的源码了,上一次是在【创建NioEventLoop】。